Safety Glasses and Face Protectors
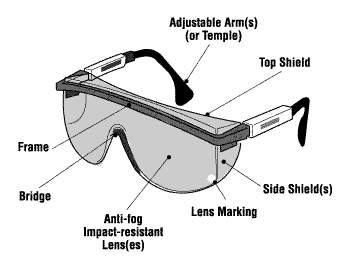
How do I recognize safety glasses?
Lenses: CSA-certified safety glasses must meet the criteria for impact resistance outlined in the standard. Safety glasses are made of polycarbonate or CR39 (plastic) or Trivex.
Markings on safety glasses: The manufacturer or supplier logo is marked (or etched) on all approved safety lenses, frames (front and temple), removable side shields, and other parts of the glasses, goggles, or helmets.
Frames: Safety frames are stronger than street-wear frames and are often heat resistant. They are also designed to prevent lenses from being pushed into the eyes.
What are the pros and cons of the different lenses?
| Comparison of Lens Materials | |
|---|---|
| Material | Characteristics |
| Polycarbonate |
|
| Plastic (CR39) |
|
| Trivex |
|
| Glass |
|
From: CSA Standard Z94.3.1-09 Selection, use and care of protective eyewear, 2009.
What is the difference between plastic and polycarbonate?
The "standard plastic" lenses in safety glasses are often called "Hard Resin", "CR-39 plastic", or just "plastic" lenses. CR-39® is actually a PPG Industries registered trade name for a DADC (diallyl diglycol carbonate) polymer that was introduced in 1941. The "CR" stands for Columbia Resin and CR-39 was the 39th batch or formula made by Columbia Laboratories in Ohio. This polymer is a polycarbonate but its starting materials are different from the resins used in safety glasses with "polycarbonate" lenses. The hard resin or CR-39 plastic is a thermoset plastic meaning it cannot be molded or bent when heated.
On the other hand, the polycarbonate polymers (e.g., Lexan®, a GE trade name) are thermoplastic which means that the lenses can be formed by melting polycarbonate pellets and injecting them into a mold.
What should I know about the fit and care of safety glasses?
If eye protection is required, establish a complete eye safety protection program including selection, fit testing, training, maintenance and inspection.
Fit
- Ensure your safety glasses fit properly. Eye size, bridge size and temple length all vary. Safety glasses should be individually assigned and fitted.
- Wear safety glasses so that the temples fit comfortably over the ears. The frame should be as close to the face as possible and adequately supported by the bridge of the nose.
Care
Safety glasses need maintenance.
- Clean your safety glasses daily. Follow the manufacturer's instructions. Avoid rough handling that can scratch lenses.
- Scratches impair vision and can weaken lenses.
- Store your safety glasses in a clean, dry place where they cannot fall or be stepped on. Keep them in a case when they are not being worn.
- Replace scratched, pitted, broken, bent or ill-fitting glasses. Damaged glasses interfere with vision and do not provide protection.
- Replace damaged parts only with identical parts from the original manufacturer to ensure the same safety rating.
What should I know about lens colours?
Lenses can be clear, tinted, photochromic or polarized. Each type offers various levels of ultraviolet protection, including no protection (even when coloured). Do not be fooled by the colour of the lenses.Conduct a hazard assessment to identify the hazards that workers may be exposed to, and then select appropriate PPE when engineering controls or other more permanent methods of control are not possible. Consult with the PPE manufacturer about the uses and limitations for each type of eye or face protection.
How do I select the proper safety glasses and face protection?
If you are at risk for eye or face injury at work, you should wear appropriate protection.
To select the proper protectors follow the recommendations in the table below.
| Selection of Eye and Face Protection | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note: This table cannot cover all possible hazards and combinations that may occur. Examine each situation carefully and select the appropriate protector or combination of protectors.
*indicates recommended protection |
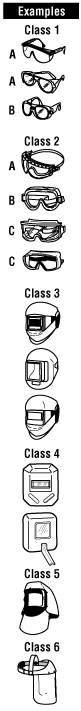 |
||||||||||||||
| A | B | A | B | C | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | ||||
| Flying Objects | |||||||||||||||
| Chipping, drilling, scaling, grinding, polishing, buffing, riveting, punching, shearing, hammer mills, crushing, heavy sawing, planning, wire and strip handling, hammering, unpacking, nailing, punch press, lathework, etc. | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Flying particles, dust, wind, etc. | |||||||||||||||
| Woodworking, sanding, light metal working and machining, exposure to dust and wind, resistance welding (no radiation exposure), sand, cement, aggregate handling, painting, concrete work, plastering, material batching and mixing | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Heat, sparks and splash from molten materials | |||||||||||||||
| Babbiting, casting, pouring molten metal, brazing, soldering, spot welding, stud welding, hot dipping operations | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Acid splash, chemical burns | |||||||||||||||
| Acid and alkali handling, degreasing, pickling and plating operations, glass breakage, chemical spray, liquid bitumen handling | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Abrasive blasting materials | |||||||||||||||
| Sand blasting, shot blasting, shotcreting | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Glare, stray light (for reduction of visible radiation) | |||||||||||||||
| Reflecting, bright sun and lights, reflected welding flash, photographic copying | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Injurious optical radiation (moderate reduction of optical radiation) | |||||||||||||||
| Torch cutting, welding, brazing, furnace work, metal pouring, spot welding, photographic copyring | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Injurious optical radiation (large reduction of optical radiation) | |||||||||||||||
| Electric arc welding, heavy gas cutting, plasma spraying and cutting, inert gas shielded arc welding, atomic hydrogen welding | * | * | |||||||||||||
From: CSA Standard Z94.3-07 (R2014) Selection, use and care of protective eyewear, 2014.
Newer articles
Older articles